
- Shandong Microwave Machinery Co.,Ltd.
- To be the Leader of microwave drying and edible oil refining equipments Manufacturer
Home> Company News> Effects of drying methods and refrigeration conditions on the content of main active ingredients in Cordyceps militaris
- AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Factory AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Phone(Working Time)+86 0531 85064681
- Phone(Nonworking Time)0086-15020017267
- Fax+ 86 0531 85064682
Effects of drying methods and refrigeration conditions on the content of main active ingredients in Cordyceps militaris
2019-01-15 14:34:19ABSTRACT: Cordyceps militaris was inoculated with silkworm larvae as host and cultivated artificially to obtain Cordyceps militaris. Cordycepin and adenosine in Cordyceps militaris were determined by different drying methods and refrigeration conditions.
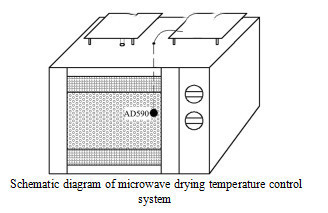
Fresh Cordyceps militaris was treated with microwave drying equipment. The content of cordycepin was higher when microwave power was 900 W and 720 W (P<0.01), and the content of adenosine was the highest when microwave power was 900 W (P<0.01). Fresh Cordyceps militaris was dried at high temperature, and the content of cordycepin was the highest when drying temperature was 60 C (P<0.01), and the content of cordycepin was the highest when drying temperature was 100 C. The content of adenosine was the lowest (P < 0.01) and the highest (P < 0.01) when the drying temperature was 70 C. Compared with microwave drying, high temperature drying, freeze drying and indoor shade drying, the content of cordycepin and adenosine in Cordyceps militaris treated by microwave drying was the highest (P < 0.01).
The contents of cordycepin and adenosine in fresh Cordyceps militaris decreased significantly (P < 0.01) after 10-20 days of cold storage at 0-5 C. militaris, while the contents of two active ingredients did not change significantly (P > 0.05) after 20 days of cold storage (P > 0.01); the contents of two active ingredients in treated Cordyceps militaris at 8 C for 10 days were significantly higher than those in treated at 5 and 0 C In practical application, microwave drying conditions should be set for different target products to process Cordyceps militaris. If cold storage and fresh-keeping treatment is selected, the appropriate temperature is 5-8 C, and the time should not exceed 10 days, so as to maximize the retention of the required medicinal active ingredients.
Key words: microwave drying of Cordyceps militaris; cordycepin; adenosine; drying method; cold storage

Cordyceps militaris is one of the most popular nutritional supplements in East Asia. It not only has similar morphology and chemical composition with Cordyceps sinensis, but also can be cultivated artificially. Large-scale production of Cordyceps militaris has been realized by using silkworm larvae or pupae as host. Cordyceps militaris is rich in a variety of bioactive substances, including nucleosides such as adenosine, cordycepin and other important medicinal active ingredients. The content of these two active ingredients in Cordyceps militaris is an important index to evaluate the quality of Cordyceps militaris.
It is reported that cordycepin has been put into clinical trial in the United States as a new anti-cancer and anti-virus drug, and a new drug for leukemia synthesized from Cordyceps militaris in China has entered a phase of clinical trial. In order to improve the quality of Cordyceps militaris products, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has been used to study the effects of cordycepin and adenosine content in Cordyceps militaris products by strains, culture medium, origin, season and parts of Cordyceps militaris. However, there are no reports on the effects of drying methods and refrigeration conditions on cordycepin and adenosine content in Cordyceps militaris products.
In this experiment, silkworm larvae were used as hosts to cultivate Cordyceps militaris artificially. The contents of cordycepin and adenosine were used as the indexes to study the drying processing methods and refrigeration conditions of Cordyceps militaris, in order to provide technical reference for the production of high-quality Cordyceps militaris products.
 High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line
High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line
Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line used deformered bar rolling mill production line
used deformered bar rolling mill production line Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line
Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply
Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply