
- Shandong Microwave Machinery Co.,Ltd.
- To be the Leader of microwave drying and edible oil refining equipments Manufacturer
Home> Company News> Effects of drying methods on the content of functional components and antioxidant activity of Scutellaria baicalensis
- AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Factory AddressNo. 225, Huangqiao Village, Beiyuan, Tianqiao District, Jinan, Shandong, China
- Phone(Working Time)+86 0531 85064681
- Phone(Nonworking Time)0086-15020017267
- Fax+ 86 0531 85064682
Effects of drying methods on the content of functional components and antioxidant activity of Scutellaria baicalensis
2019-01-04 16:47:52
ABSTRACT: OBJECTIVE: To investigate the suitable drying methods of Radix Scutellariae by taking the contents of total polysaccharides, total phenols, total flavonoids, VE with different configurations and antioxidant activity as indicators.
METHODS: The contents of total polysaccharides, total phenols, total flavonoids and antioxidant activities were determined by ultraviolet spectrophotometry, and the contents of VE in different configurations were determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The effects of six different drying methods (shade drying, sun drying, drying, vacuum freeze drying, infrared drying, microwave drying) on the quality of Euphorbia chinensis were evaluated comprehensively.
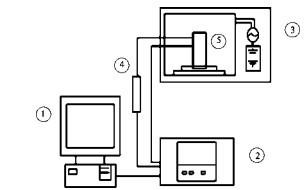
RESULTS: Microwave drying equipment could preserve the total polysaccharides, phenols and flavonoids to the greatest extent. Under vacuum freeze-drying conditions, the content of VE in different configurations was the highest and scavenged 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrophenylhydrazine (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, DPPH) free radicals, 2,2'-biazo (3-ethyl-benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt was free. (2,2'-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate), ABTS + had the strongest ability; correlation analysis showed that the content of VE in different configurations was significantly correlated with antioxidant activity.
CONCLUSION: Vacuum freeze-drying has the best antioxidant activity on the basis of maximizing the accumulation of various VE configuration components, and reduces the loss of total polysaccharides, total phenols and total flavonoids to a certain extent. It can be used as an appropriate drying method for the processing of Scutellaria baicalensis.
Key words: drying method; microwave drying of Scutellaria baicalensis; functional components; antioxidant activity

Scutellaria is the dry and mature seed kernel of the annual aquatic vascular plant Scutellaria in the water lily family, also known as Chicken Head Rice and Chicken Head Lotus. It was first published in the Shennong Herbal Classic and was listed as the top grade. It was later included in the Pharmacopoeia of previous editions.
Scutellaria baicalensis is native to China and Southeast Asia, widely distributed in southern China, mainly in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Heilongjiang and other places. It grows in lakes, ponds, beaches and ditches. It is covered with dark black seed coat. After being salvaged in late autumn and winter, it strips its hard seed coat and exposes seeds with red skin. It has the functions of nourishing kidney, reinforcing spleen, stopping diarrhea, dispelling dampness and stopping bands. Scutellaria baicalensis mainly contains VE, flavonoids and polyphenols with different configurations, which have certain anti-aging and lipid peroxidation effects, so it has good market prospects in the application of functional food.
Origin processing is an important link in the production and quality formation of medicinal materials. It includes the separation of medicinal and non-medicinal parts, the maximum retention of functional and nutrient components, the minimization of toxic and harmful substances, the transformation of chemical components and other physical and chemical properties. The ultimate goal is to produce high-quality medicinal and non-medicinal parts, which can improve the effectiveness and safety. Medicinal materials.
In recent years, the research on drying methods of Scutellaria baicalensis mainly focused on the effects of different temperatures on water content and drying rate of Scutellaria baicalensis during atmospheric and vacuum drying, and discussed the law of water distribution between Scutellaria baicalensis and its shell. However, few studies have been done on the effects of drying methods on functional components and antioxidant activities of Scutellaria baicalensis, and the drying methods are traditional and single.
 High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line
High efficiency food beverage factory stone paper production line Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line
Factory price Fully automatic Machine PP/PS Plastic Sheet Production Line used deformered bar rolling mill production line
used deformered bar rolling mill production line Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line
Manufacturing plant automatic factory puffed sticky rice cracker production line Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply
Production Line Pp Ppr Plastic Pipe Making Machine 20-63mm Multi-layer Extrusion Production Line For Water Supply